Introduction
A device on the internet or on a local network is identified by its IP address, which is a unique address on that particular network. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a set of rules that regulate the format of data transferred over the internet or a local/private network.
IP addresses, in essence, are the identifiers that allow data to be transmitted between devices over a network: they contain location information and make devices reachable for communication. The internet needs a method of distinguishing between various computers, routers & webpages. IP addresses are essential aspect of how the internet operates and provide a means of doing so.
What is an IP?
IP address/Internet Protocol address, is an identifying number which is related to a specific computer, when connected to other computers or a network. The IP address allows the computers/devices to send and receive information. The IP address allows the computers to send and receive information. IP addresses are made up of four numbers; for example, 192.168.1.251 is an example address. This set's numbers can vary from 0 to 255. As a result, the entire IP addressing can be ranged from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255.
IP addresses are not generated randomly. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), a part of the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), creates and assigns IP address mathematically. ICANN is a non-profit organization build in the United States, founded in 1998 to assist keep the internet secure and accessible to everyone. A domain name registrar is used every time someone registers a domain on the internet, and assign domain names a IP address.
How IP addresses work?
It helps to understand how IP addresses function if you want to figure out why a device isn't connecting the way you want it to or if you want to troubleshoot why your network isn't working.
Internet Protocol communicates in the same manner that any other language does, by following a set of rules to convey information. This protocol is used by all devices to find, send, and share information with other connected devices. Any computer in any area in the world can communicate with one another if they speak the same language.
IP addresses are most commonly used behind the scenes. The procedure is as follows:
- Your device connects to the internet indirectly by first connecting to a network linked to the internet, which then allows your device internet access.
- That network will most likely be your Internet Service Provider when you are at home (ISP). It will be your workplace network at work.
- Your Internet service provider (ISP) assigns an public IP address to your device.
- Your internet activity passes through your ISP, which uses your public IP address to deliver it back to you. It is their responsibility to issue an IP address to your device because they are providing you with an internet connection.
- Your IP address, on the other hand, may change. Turning your modem or router on or off, for example, can make a difference. You can also contact your ISP and get it changed for you.
- Your home IP address does not go with you while you are out and about – for example, when you travel – and you take your device with you. This is because you will be accessing the internet through a different network (Wi-Fi at a hotel, airport, or coffee shop, for example) and will be allocated a different (temporary) IP address by the hotel, airport, or coffee shop's ISP.
As the name says, there are various types of IP addresses, which we are going to discuss further below.
There are various types of IP addresses, as well as distinct categories of IP addresses.
- Private IP Addresses
- Public IP Addresses
- Dynamic IP Addresses
- Static IP Addresses
Private IP Addresses
A private IP address is assigned to any device that connects to your home network. Computers, phones, and other IoT devices are included, as well as any Bluetooth-enabled devices such as speakers, printers, and smart TVs. The number of private IP addresses, you have at home is likely to increase as the number of internet of things grows. Your router must be able to detect each of these devices separately, and many of them must be able to recognize one another. As a result, your router generates private IP addresses for each device, which helps to identify a particular device on your home network.
Public IP Addresses
Public IP address is the primary address associated with your whole home network. While each connected device has its own private IP address, they are all part of your network's primary IP address (Public IP Address). Your ISP provides the public IP address for your router, as explained above. ISPs typically have a big list of IP addresses from which to assign addresses to their clients. Your public IP address is the address that will be used by all devices outside your internet network (outside of home network) to identify your home network.
Public IP address have two types Dynamic and Public.
Dynamic IP Addresses
As the name says, IP addresses that are dynamic change on a regular basis. Usually an ISP (Internet Service Provider) purchase a big pool of IP addresses and assign them to their clients automatically. They re-assign them on a regular basis, and the older IP numbers are returned to the pool to be used for other users. This rationale behind this strategy is to save money for the ISP. Your ISP don't have to perform specific procedures to re-establish a customer's IP address if they move house. for an example, because the routine transfer of IP addresses is automated. There are also security advantages, as a changing of IP address makes it more difficult for hackers to maintain access to your network interface, even the hacker compromised it.
Static IP Addresses
Static IP addresses, unlike dynamic IP addresses, did not change. Once an static IP address is assigned by the network, it does not change. A static IP address is not required for most individuals and businesses, but it is required for businesses/individuals who plan to host their own server. This is because a static IP address ensures that the websites and email addresses associated with it have a stable IP address, which is essential if you want that other devices to be able to find them on the internet consistently. You can talk to your ISP for static IP address if required. Sometimes gamers (MineCraft) uses static IP addresses to host online game servers.
What is the best way to look up IP addresses?
The most straightforward way to determine your router's public IP address is to Google "What is my IP address?" The solution will be displayed at the top of the page by Google.
Other websites will display the same information: they will be able to see your public IP address because your router has made a request and so released the information by visiting the site. IP Location takes a step further by displaying your ISP's name as well as your city.
In most cases, this technique will only provide an approximation of position – where the provider is, but not the exact location of the device. Remember to log out of your VPN as well if you're doing this. Obtaining the public IP address's true physical geographical address is frequently difficult.
Finding your private IP and private IP address on Linux system is very easy, we need to run following command on our terminal
The above command will show our private IP address. To find our public IP address we can search Google as we said previously, or we can run following command on our terminal:
In the following screenshot we can see the output of both commands:
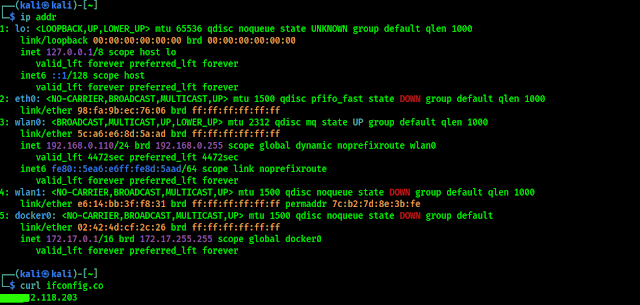 |
| For privacy reasons we hide our part of public IP address |
Summary
To conclude, IP addresses come in many types and for many situations, but all follow the same procedure. Whether it's locally assigned or it has come from your ISP, IPs are a consistent and necessary part of computer networking.
