In our this article we are going to learn about how we can deal with files directly from our terminal window.
But did we must have to learn this? Because Kali Linux and other most popular Linux distributions comes with good graphical user interface (GUI), so why we need to learn how to something with a file from command line where we can do it just like we do on Windows system?
Well in our opinion when we are reading this on this website then we have interest on cybersecurity field. When we are dealing with an remote system (read compromising a system) we have to do it on terminal. We need to break the privileges and get into it. There are lots of things with file we need to do here (from modifying system file data to uploading shells). So we need to have at-least a basic idea to dealing with files from terminal.
Creating a File using Terminal
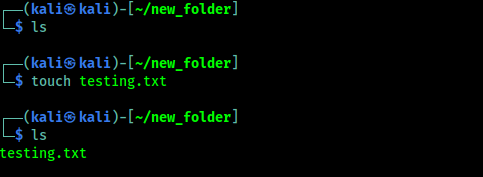
First we will learn how we can create a file on Linux terminal. We will going to use touch command. We just need to run touch filename command to create a file. As shown in the following screenshot:
Copy Files using Terminal
We can copy files/directory from a directory to another one by using terminal window. To do that we need to use cp command. Suppose we have a file on our /home/kali/desktop directory. We need to copy this file to /home/kali/new_folder directory. We use following command for that:
As we can see in the following screenshot:
In the following screenshot we can see that our file is copied to our destination directory. We did this for a file only we can do the same for a folder/directory.
Moving Files using Terminal
We can move a file from a directory to another directory to other directory by using mv command. This is very similar like cp command. mv full/path/of/file destination/path as we can see in the following screenshot:
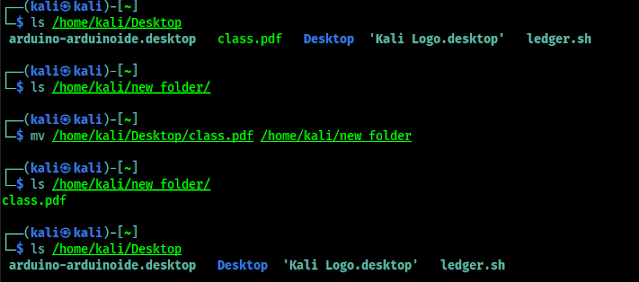 |
| Our file is moved from source directory |
Renaming Files using Terminal
Basically we move a file/directory on the same directory and change the name. That is what renaming do. The mv command to change the name of a file without moving it to another directory.
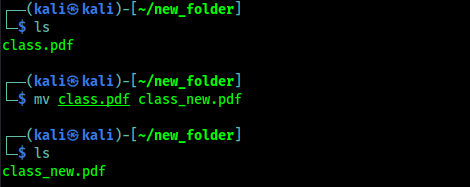 |
| We can see that we renamed the file |
Deleting Files using Terminal
We also can delete a file directly from terminal by simply using rm command. We just need to rm filename command to delete any file. To delete a file forcefully we need to use -f flag -r flag used to remove contents recursively.
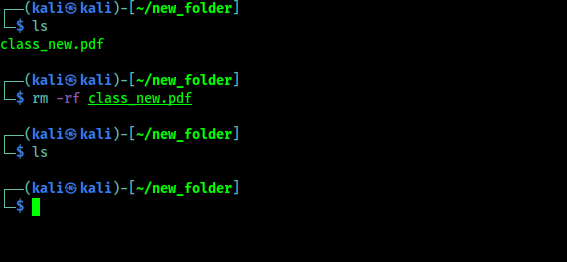 |
| Deleting files using Terminal |
Editing Files using Terminal
Let we have take look at file editing in terminal. As we told that this is too much important to have Linux skill, especially during the pen-testing if we need access to a Linux or UNIX based OS or server.
There are some cool text editors like gedit, leafpad and mousepad, they may looks far better than command line text editors for their graphical user interface, but we will focus on terminal based text editors. Everyone might have their own favorite text editors, but here we are going to cover two most common options, Nano and Vi.
Nano
Nano is the most user friendly and simplest text editors. To open a file and start editing we simply run nano <file name>.
After the file opened we can start editing the text as we can do on any graphical user interface using keyboard. As we can see in the following screenshot:
 |
| Editing text using nano text editor on terminal |
If we see in the bottom of following screenshot, we can see the command menu there. We need to memorize some widely used keyboard shortcuts like:
- CTRL+O - Write changes to the file.
- CTRL+K - Cut to Current Line.
- CTRL+U - Uncut a line, and paste it at the cursor location.
- CTRL+W - Search
- CTRL+X - Exit
To know more about nano, we need to see it's official documentation.
vi
vi is very powerful text editor with it's lightning speed, especially when it comes to automated repetitive tasks. However, it has a relatively sleep learning curve and is nowhere near as simple to use as Nano. It is so much complex so we cover the basis only. Similar to nano, to edit a we need to run vi filename command.
After the file is opened, we need to enable the insert-text mode to begin typing. To do this, we need to press I key and start typing and editing file.
To disable insert-text mode and go back to command mode, we need to press Esc key. In command mode we can use following command to use it.
- dd - Delete the current line.
- yy - Copy the current line.
- p - Paste from clipboard.
- x - Delete the current character.
- :w - Write the current file to disk and stay in vi.
- :q! - Quit without saving.
- :wq - Save and Quit.
vi is extremely powerful, Want to explore vi ? The following sources have very good manual to learn vi.
Comparing Files using Terminal
Comparing files may seems irrelevant for normal users, but system admins, network engineers, penetration testes and other IT related professionals rely on this skill widely.
In this section, we'll take a look at a couple of tool that can easily help us during file comparing.
comm
The comm utility compares between two text files then displays the lines that are unique to each one, also shows the lines they have in common. comm outputs three space-offset columns. The first column will be the output unique lines of the first file. The second column will contain unique lines of the second file, and the third column contains lines that are shared by both files.
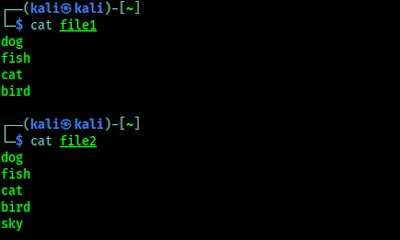
For an example here we have two files "file1" and "file2", these files contains some words, as we can see in the following screenshot:
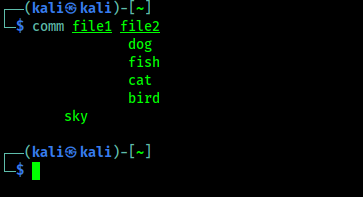
Now we are going to compare these two files using comm command. So we are going use following command:
The output of the above command shown in the following screenshot:
In the above screenshot, we can see that it compares both files.
Vimiff
The vimdiff command opens with multiple files, on in each window. It also shows the differences between files by highlighting them. Which makes easier to find the differences between files. So we run the command as following:
We can see the output in the following screenshot:
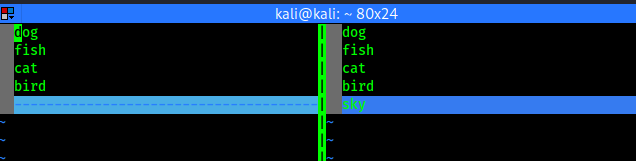 |
| We can notice the differences easily for highlighted area. |
- do: Get changes from the other window to current window.
- dp: Sends the changes from current window to another window.
- ]c: Jumps to the next difference.
- [c: Jumps to the previous difference.
- CTRL+W: Switches to the other split window.
Downloading Files using Terminal
Now we are going to take a look on downloading files using terminal. For downloading files we are going to use wget and curl.
wget
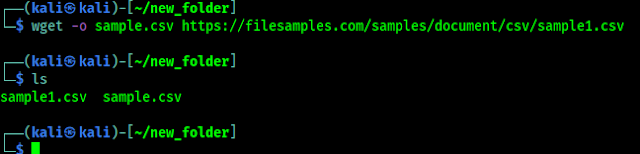
The wget command, which we will use extensively, downloads files using the HTTP/HTTPS and FTP protocols. We can use wget url/of/file to download a file.
In the above screenshot we had download a file using wget and -o flag to make a copy of the downloaded file our chosen name.
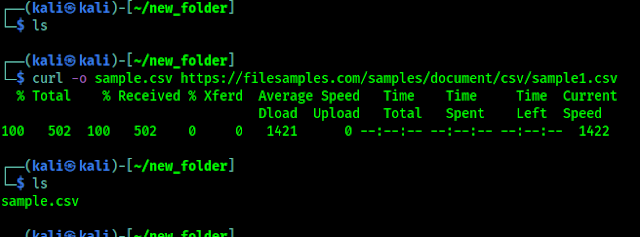
curl
curl is a tool for transferring data to a server or from a server using host protocols including IMAP/S, POP3, SCP, SFTP, SMB/S, SMTP/S, TELNET, TFTP and others. A penetration tester can use curl to upload things (read payload) on server, or download things from server, and build complex requests. Basic use of curl is very similar to wget.
axel
axel is a download accelerator that transfers a file from a FTP or HTTP server through multiple connections. axel has a vast array of features, but the most common feature is almost similar to wget and curl. We also can use -n flag, which is used to specify the number of multiple connections to use.
This is how we can manage files directly from Linux terminal. In this article, we learnt how we can copy, move, rename, delete, edit, compare and download files on Linux or UNIX like system. We don't need GUI for this. Learning these things are very important for cybersecurity students.
Love our articles? Make sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub, we post article updates there. To join our KaliLinuxIn family, join our Telegram Group. We are trying to build a community for Linux and Cybersecurity. For anything we always happy to help everyone on the comment section. As we know our comment section is always open to everyone. We read each and every comment and we always reply.